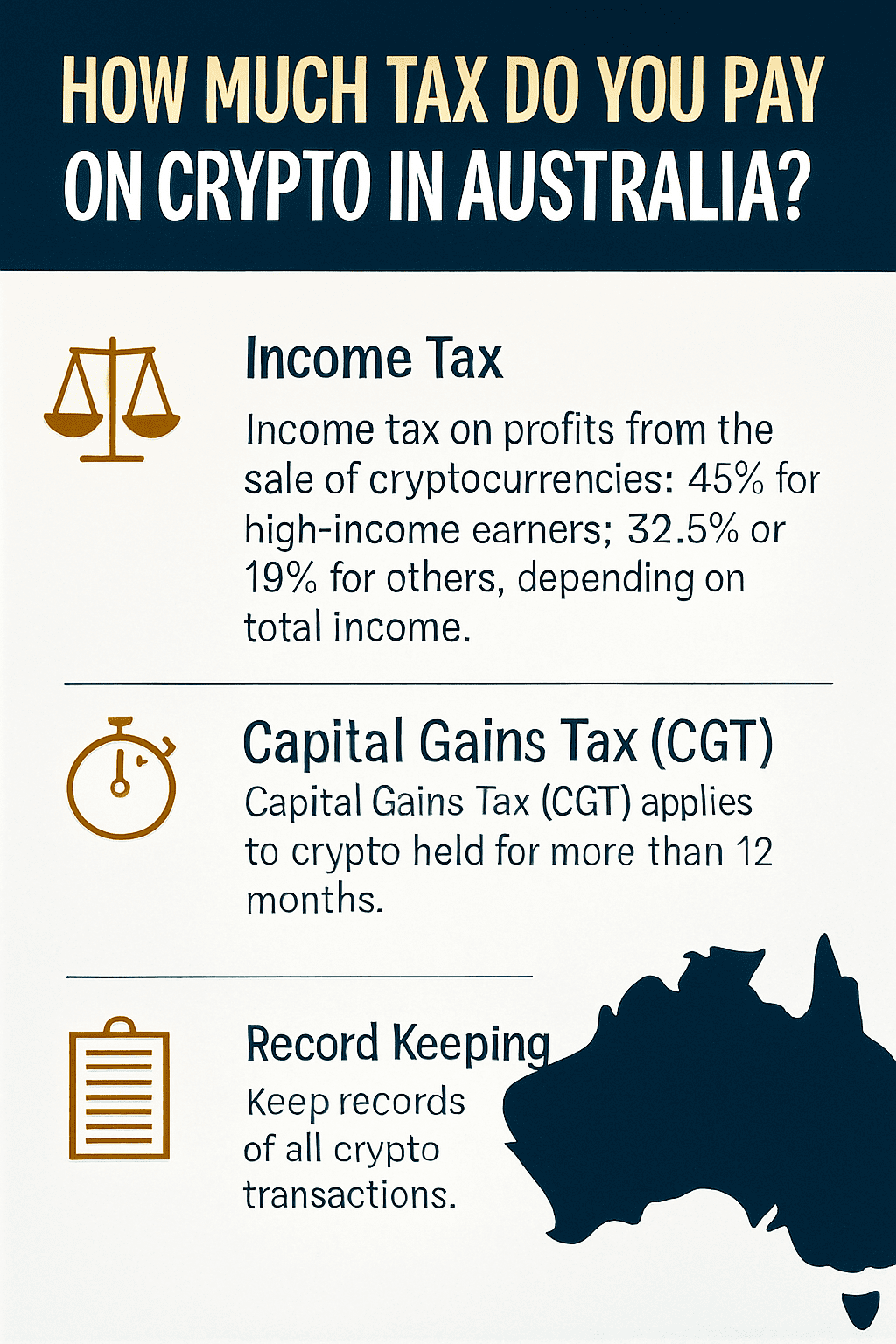
Cryptocurrency has become more popular in Australia, but understanding the taxes is vital for each trader and investor.
The Australian Taxation Office (ATO) treats cryptocurrency as property, therefore CGT (Capital Gain Tax) or ordinary income tax applies to profit gained from trading, mining, or disposing digital assets.
As a professional trader, investor, or hobbyist, knowing how much tax you owe will ensure you stay compliant, and it will allow you to efficiently plan your crypto activities.
Overview of Cryptocurrency in Australia
Cryptocurrency in Australia is becoming more popular quickly as more people trade and invest in Bitcoin and Ethereum. The government classifies crypto as property, so profits generated from crypto will incur Capital Gains Tax.

Crypto exchanges are also required to follow AUSTRAC regulations The rise in adoption is driven by the interest of retail and institutional investors, the clear regulations, and a strong fintech ecosystem. Banks are slow to support crypto, but the ecosystem is strong.
How Much Tax Do You Pay on Crypto in Australia?
Your income bracket determines how much tax you pay on capital gains and regular income. Here are the 2024-2025 financial year tax ranges in Australia.
| Income Thresholds (AUD) | Rate | Tax Payable on This Income |
|---|---|---|
| $0 – $18,200 | 0% | Nil |
| $18,201 – $45,000 | 16% | 16c for each $1 over $18,200 |
| $45,001 – $135,000 | 30% | $4,288 plus 30c for each $1 over $45,000 |
| $135,001 – $190,000 | 37% | $31,288 plus 37c for each $1 over $135,000 |
| $190,001 and over | 45% | $51,638 plus 45c for each $1 over $190,000 |
Long-term capital gains: In Australia, income from the collection or disposal of cryptocurrency which is longer than 12 months qualifies for a 50% discount. Meaning, half of your capital gain is considered taxable income.
When To Report Crypto Taxes In Australia?
In Australia, the tax year runs from July 1 to June 30 of the next year. Let’s say you’re filing a tax return for the year July 1, 2024, to June 30, 2025; that return will be due October 31, 2025. But, if you’re filing through an accountant, you have an extension until May 15, 2026, to file that return.
What tax rates do traders pay on cryptocurrency?

Most people buying and selling cryptocurrency in Australia are classified as investors. But if you are engaging in trading crypto in a manner described by the ATO as ‘organized, business manner’, then you are a trader.
Trader Taxation: For cryptocurrency profit being taxed, traders are taxed at the same income tax rate as an investor. The difference is, unlike investors, traders do not get a 50% discount on capital gains tax for assets held for more than a year.
Benefit of being a trader: a trader can deduct expenses related to their trading like internet costs or software expenses, which an investor cannot.
The difference between a trader and an investor can sometimes be slight. If you are in doubt, consult the ATO’ s guidelines for your classification.
Tax Obligations for Crypto Miners in Australia
Identify Type of Mining Activity: Hobby vs Business: Tax rates differ based on whether you mine cryptocurrency as a hobby versus as a business.
Determine Fair Market Value (FMV): When you received the mined token, calculate the FMV. This value is used for income reporting and the future calculations of the Capital Gains Tax (CGT) on your token.
Assess Expenses for Mining: Assess all expenses for mining cryptocurrency, including any electricity, hardware, software, and mining pool fees.
Calculate Net Taxable Income:
$$\text{Taxable Income} = \text{FMV of Token} – \text{Mining Expenses}
For hobby miners: the token mined is not subject to tax, but CGT is incurred on the sale or disposition of the token.
For business miners: the mining income is treated as ordinary income, and expenses related to mining income can be used to lower the taxable income.
Example:
- Harry mines 1 BTC worth AUD 500 as a hobby. No tax is due immediately, but CGT is applies when Harry sells the token.
- Barry operates a BTC mining business, generating worth AUD 50,000. After setting up his mining rigs and incurring electricity expenses, which total AUD 15,000, he receives a net taxable income of AUD 35,000 (50,000 – 15,000) which is taxed as ordinary income.
Is cryptocurrency legal in Australia?
Yes, cryptocurrency is legal in Australia. Cryptocurrency is however taxed as property. All cryptocurrency exchanges in Australia must register with AUSTRAC as a financial service provider.
Tax on Donations of Crypto in Australia
Donating cryptocurrency is an associated Capital Gains Tax (CGT) Event. This is similar to selling or exchanging an asset. It is important to calculate any capital gain or loss based on the value of the crypto at the time of donation.
Deduction for Donations
- Donations to Deductible Gift Recipients (DGRs) can qualify for a tax deduction. Plus, any capital gain on the donated crypto is generally CGT-free.
- Deductions will not be allowed in the following scenarios:
- Testamentary gifts (gifts made under a will)
- Donations to the Cultural Gifts Program
- Crypto classified as a personal use asset
Determine Tax on a Donation of Crypto
- Determine Cost Basis. The FMV of the token at acquisition (purchase, mining, or staking) will need to be determined.
- Determine FMV at Donation. The FMV of the crypto to be donated will need to be noted.
- Calculate Capital Gain/Loss:
\text{Capital Gain} = \text{FMV at Donation} – \text{Cost Basis}
Example:
On July 1, 2022, Adam purchased 1 BTC for AUD 10,000. He donated it to a school (not a DGR) on May 3, 2023, and it was valued at AUD 30,000. He also had a transaction fee of AUD 100.
- Cost base: 10,000 + 100 = AUD 10,100
- Capital gain/loss: AUD 30,000 (he donated it so no gain) – 10,100 = 19,900 (this is gain for capital gain tax calculation)
Using the income tax slab, the tax-free threshold is AUD 18,200:
- 19,900 – 18,200 = 1,700 (this is the amount taxed, the rest exemption)
- 19% = 323 (this is the capital gain tax payable)
Tax-free crypto
To wrap up, there’s no need to stress; some crypto activities are still tax exempt. For example, buying and holding crypto, and even receiving crypto as a gift, are some tax exempt activities. However, things can get tricky with tax exempt situations as well, especially in DeFi transactions, and distinguishing between being an ‘investor’ or ‘trader’.
In general, specifically with Australian tax laws, here are situations where no tax is required for crypto activities:
- Buying crypto in Australian dollars
- Holding crypto
- Receiving crypto as a gift
- Crypto hobby mining
- Wallet to wallet crypto transfers, just as a heads up, there are transfer fees
- Spending crypto to pay for personal use and for goods and services
- Charitable donations in crypto to nominated DGR entities
Conclusion
In Australia, cryptocurrency gains are taxed under the Capital Gains Tax (CGT) regulations. When it comes trading, mining, or disposing of cryptocurrencies, the gains will be included in your taxable income. For holdings under 12 months, the gains will be taxed at your income marginal rate.
Zero to less than three year holdings may be considered for a 50% CGT long term discount. For traders, if the crypto is treated as a business, ordinary income tax will be applicable and the business expenses will be deducted.
Donations in crypto to registered Deductible Gift Recipients (DGRs) may also trigger tax deductions especially in CGT liability. Good record keeping will assist in acquisition cost calculation, and determining fair market expenses to be deducted when it comes to tax will be required.
FAQ
Cryptocurrency is treated as property for tax purposes. Profits from buying, selling, or trading crypto are generally subject to Capital Gains Tax (CGT). Mining income and trading in a business capacity are taxed as ordinary income.
Short-term gains (held ≤12 months) are taxed at your marginal income tax rate (0%–45%).
Long-term gains (held >12 months) may get a 50% CGT discount.
Donating crypto is considered a CGT event. Donations to Deductible Gift Recipients (DGRs) may allow a tax deduction, and CGT may not apply.
Mining rewards are treated as ordinary income at the fair market value when received. Related mining expenses can be deducted if conducted as a business.
No tax is due until you sell, trade, or dispose of the crypto. Gains are calculated at that time for CGT purposes.