This article focuses on “Bitcoin Security Best Practices For Large Holders” to secure considerable digital assets against theft, hacks, and losses.
Security becomes paramount when one holds large quantities of Bitcoin, as it is accompanied by unique dangers.
From cold storage and multi-signature wallets to the management of keys, the appropriate measures guarantee safety and accessibility of assets at all times.
Key Points & Bitcoin Security Best Practices For Large Holders
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Use Cold Storage | Store the majority of funds offline in hardware wallets or paper wallets to protect against online hacks. |
| Multi-Signature Wallets | Require multiple private keys to authorize transactions, reducing single-point-of-failure risk. |
| Hardware Wallets Only | Use reputable hardware wallets and avoid software wallets for large holdings. |
| Secure Private Keys | Never share private keys; store backups in safe, geographically separate locations. |
| Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) | Enable 2FA on all exchange and wallet accounts to prevent unauthorized access. |
| Use Trusted Exchanges | Only interact with reputable exchanges for trading or converting, avoiding unregulated platforms. |
| Regular Software Updates | Keep wallet firmware and related software updated to patch security vulnerabilities. |
| Avoid Public Wi-Fi | Never access wallets or exchanges over unsecured networks; use VPN if necessary. |
| Diversify Storage Locations | Split funds across multiple wallets or storage solutions to minimize risk. |
| Plan for Inheritance & Recovery | Ensure a secure plan for heirs to access funds in case of death or loss of keys. |
10 Bitcoin Security Best Practices For Large Holders
1. Use Cold Storage
While keeping Bitcoin “cold” entails not storing Bitcoin on any internet connected devices, it primarily means putting Bitcoin on devices that are kept away from any internet.
For those that hold considerable Bitcoin, the chances of hacking, phishing, and malware attacks are severely reduced.

This can be done with hardware and paper wallets or air-gapped computers. Cold storage should be used for long term storage to make sure the money isn’t exposed to online threats.
2. Multi-Signature Wallets
Multi-signature wallets require several private keys to be accessed to finalize any transaction, often from a different device or user.
This means that the chances of losing a key and allowing unauthorized transactions is reduced to a minimum, as the user would still need to obtain all keys to complete a transaction.
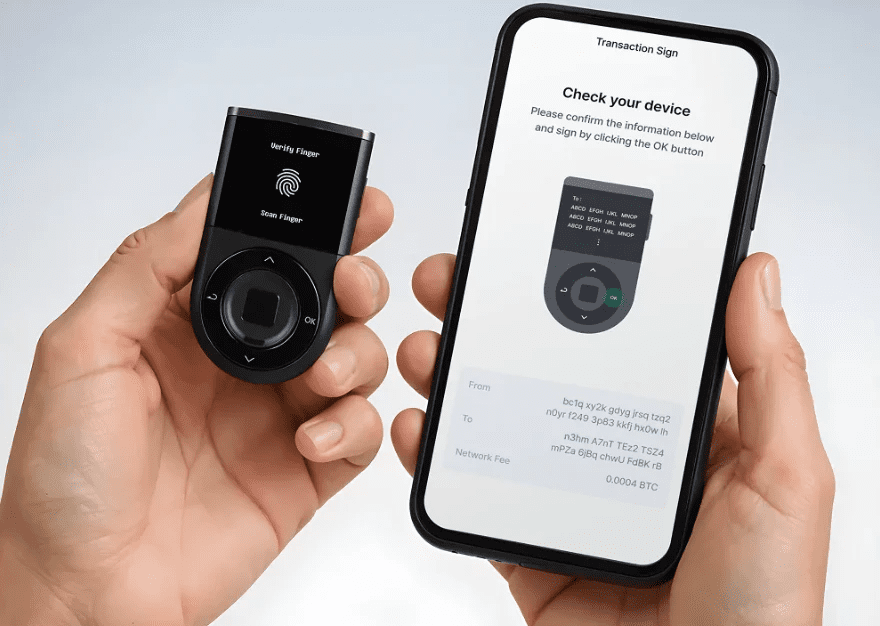
Multi-sign wallets are designed for those that hold considerable amounts of Bitcoin and wish to insure it against theft or possible loss, as it will be unable to access the keys.
3. Hardware Wallets Only
The purpose of a hardware wallet is to hold a person’s cryptocurrency keys offline. They sign a transaction without exposing any private keys to the computer and, thus, provides a safe layer against any phishing attack and malware.
Significant hardware and software wallets are recommended for large balance holders. To protect against counterfeit and tampered devices, purchase the hardware wallets from the manufacturer and perform regular firmware updates.

Despite the careful handling and costs of the hardware wallets, the encryption and offline system is what makes hardware wallets the most secure way to handle a large amount of bitcoins.
4. Secure Private Keys
Your private keys are the gateway to your Bitcoin and losing keys means losing access permanently. Keys must be stored offline and in secure, isolating, and fireproof containers in different areas for large holders.
Do not use digital storage for primary keys and do not use cloud services. Encrypted backups are a good way to mitigate the risks of the split storage key strategy.

Keys must be shared and placed in a casual storage system, exposing the funds to casual theft. Key management will ensure that the hold is secure and can provide safe access whenever needed. Key disasters and digital attacks will be countered with the redundant system.
5. Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) requires more than just your password to access an account. Depending on the implementation, access may also require an application code or physical token.
For large Bitcoin holders, adding 2FA on all exchanges, wallets, and email accounts is a highly recommended practice, as it helps block unauthorized access to accounts, even when credentials are entered.
2FA implementations based on cellphone networks (SMS) should be avoided since they are the target of SIM swaps. While 2FA won’t protect against every attack, it acts as a buffer against phishing, password leaks, and theft.
6. Use Trusted Exchanges
Using only reputable and regulated exchanges reduces the incidence of hacks, exit scams, and insolvency risks. Big holders are encouraged to carry out extensive due diligence by verifying an exchange’s history, security measures, insurance, and regulatory statutes.
Platforms that are unknown or unverified should be avoided, particularly those that advertise unusually high returns. While exchanges can be used to provide liquidity, it is unwise to store large amounts long-term on them.

For active trading, keep the majority of your funds in secure personal storage (like cold wallets) to ensure your security is not compromised for trading convenience.
7. Securing your Software
As a Bitcoin holder, you should ensure that your wallets, devices, and associated software are regularly updated.
Most software requires regular updates and these updates are designed to eradicate software exploits and scale protective measures.
Updates to wallets should not be neglected, especially by large holders. Malicious software and exploits could be waiting to capture your unprotected wallets.
Software updates are protective measures and, despite the inconvenience, the pros outweigh the cons. Ignoring updates and maintenance opens gateways and leaving your software unprotected may make you unsusceptible to new hacks.
8. Public Wi-Fi
Using unprotected Wi-Fi to access wallets or exchanges puts large Bitcoin holders at risk of man-in-the-middle attacks, eavesdropping, or active malware injection. Public access points and even trusted networks can be compromised. Remote access should require a VPN.
Mobile devices and laptops should have firewalls and antivirus installation so that ruthless network bullies do not claim forked valuables. Careful and mindful network use reduces exposure to cyber attacks.
Every network use needs protective measures, and simple actions should not turn into theft. Checking balances or initiating transactions are simple actions that can be theft vectors. Tight network usage should be the norm.
9. Diversify Storage Locations
Splitting Bitcoin holdings across multiple wallets, devices, or physical locations minimizes loss risk.
Thieves, natural disasters, or failure of a device can all contribute to loss, though, in the case of loss, some of the risk can be mitigated by using cold storage, multisig wallets, and geographically separated backups.

Tracking and redundancy ensure that a loss of access will not occur. Increased management complexity, however, is needed.
A protection strategy is necessary to ensure the risk of a loss of access is mitigated with a appropriate strategy and the risk is in a manageable state.
10. Plan for Inheritance & Recovery
It is necessary that high net worth holders lose access of their Bitcoin in the case of death or incapacitation.
Keys, passwords, and recovery methods are documented in a legal and escrow arrangement, and is sensitive in the case of an unexpected loss.

Clear inheritance plans and legal guidelines prevent a loss of funds to mismanagement and ensure the flow of assets to recoverable and safe storage.
Wealth protection is needed to flow across generations, and unexpected losses contain a high risk to recover.
Cocnlsuion
To conclude, protecting large amounts of Bitcoin necessitates offline storage, hardware wallets, multi-signature wallets, and rigorous key control.
Enhancing these measures with 2FA, reliable exchanges, regular software updates, cautious network interactions, diversified storage, and planned inheritance addresses potential risks from hacks, loss, and other unpredictable situations.
To safely preserve large amounts of digital assets, extensive and disciplined measures are necessary.
FAQ
Cold storage keeps Bitcoin offline, protecting it from online hacks and malware.
A wallet requiring multiple private keys to approve transactions, enhancing security.
They store keys offline and prevent exposure to malware or phishing attacks.
Store them offline, in safe locations, with encrypted backups and redundancy.
Yes, it adds an extra security layer, reducing unauthorized access risk.